| HOME | INSTRUMENTATION | NMR TIME | USERS & RESEARCH |
INDUSTRIAL AFFILIATES |
NEWS & LINKS |
Publications: Allwardt, J.R., Stebbins, J.F., and Frost, D.J.. (accepted) "The effect of composition, compression, and decompression on the structure of high-pressure aluminosilicate glasses: An investigation utilizing 17O and 27Al NMR" In Chen, J., Q. Wang, Y., Duffy, T., Shen, G., and Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Eds. Frontiers in High Pressure Research: Geophysical Applications. T. O. Sandland, L.-S. Du , J. Webster and J.F. Stebbins (in press) "Structure of Cl-Containing Silicate and Aluminosilicate Glasses: A 35Cl MAS NMR study" Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta.
L.-S. Du and J. F. Stebbins (2004) "Calcium and Strontium Hexaluminates: NMR Evidence that "Pentacoordinate" Cation Sites Are Four-Coordinated" J. Phys. Chem. B. 108, 3681-3685.
L.-S. Du, J.R. Allward, B.C. Schmidt and J.F. Stebbins (2004) "Pressure-Induced Structures Changes in a Borosilicate Glass-Forming Liquid: boron coordination, non-bridging oxygens, and network ordering" J. Non-Cryst. Solids 337, 196-200.
Allwardt, J.R., Stebbins, J.F., Frost, D.J., Schmidt, B.C. (2003) "The effect of modifier cations on the amount of five- and six-coordinated aluminum present in high-pressure aluminosilicate glasses" Bayerisches Forschunsintitut fur Experimentelle Geochemie und Geophysik, Universitat Bayreuth, Annual Report, 3.7i. Allwardt, J.R., Stebbins, J.F., and Schmidt, B.C. (2003) "Structural mechanisms of compression and decompression in high-pressure K2Si4O9 glasses" Bayerisches Forschunsintitut fur Experimentelle Geochemie und Geophysik, Universitat Bayreuth, Annual Report, 3.7h. Stebbins, J.F., Kojitani, H., Akaogi, M. and Navrotsky, A. (2003) "Aluminum substitution in MgSiO3 perovskite: Investigation of multiple mechanisms by 27Al NMR" Am. Mineral. 88, 1161-1164.
Lee, SK; Stebbins, JF; Weiss, CA; Kirkpatrick, RJ (2003) "17O and 27Al MAS and
3QMAS NMR study of synthetic and natural layer silicates" CHEMISTRY OF MATERIALS
15 2605-2613.
Lee, SK; Stebbins, JF (2003) "The distribution of sodium ions in aluminosilicate glasses:
A high-field Na-23 MAS and 3Q MAS NMR study" GEOCHIMICA ET COSMOCHIMICA ACTA
67, 1699-1709.
Kroeker, S.K., Rice, D., and Stebbins, J.F. (2002) "Disordering during melting: An
17O NMR study of crystalline and glassy CaTiSiO5 (titanite)" Am.
Mineral. 87 572-579.
Stebbins, J.F., Du, L.-S., Kroeker, S., Neuhoff, P., Rice, D., Frye, J., Jakobsen, H.J. (2002) "New opportunities for high-resolution solid-state NMR spectroscopy of oxide materials at 21.1 and 18.8 Tesla fields" Sol. St. NMR 21 105-115.
Stebbins, J.F. and Du, L.-S. (2002) "Chloride ion sites in silicate and aluminosilicate
glasses: a preliminary study by 35Cl solid-state NMR" Am.
Mineral. 87 359-363.
Kroeker, S. and Stebbins, J.F. (2001) "Three-coordinated boron-11 chemical shifts
in borates" Inorg. Chem. 40 6239-6246.
(Details Below)
Kroeker, S., Neuhoff, P.S. and Stebbins, J.F. (2001) "Enhanced resolution and
quantitation from "ultrahigh" field NMR spectroscopy of glasses" J.
Non-Cryst. Solids 293-295 440-445.
Stebbins, J.F., Oglesby, J.V., and Kroeker, S. (2001) "Oxygen triclusters
in crystalline CaAl4O7 (grossite) and calcium aluminosilicate glasses: 17O
NMR" Am. Mineral. 86, 1307-1311.
Stebbins, J.F., Kroeker, S. and Andrault, D. (2001) "The mechanism of solution
of aluminum oxide in MgSiO3 perovskite" Geophys. Res.
Lett. 28, 615-618.
(Details Below)
Stebbins, J.F., Kroeker, S., Lee, S.K. and Kiczenski, T.J. (2000) "Quantification
of five- and six-coordinated aluminum in aluminosilicate and fluoride-containing
glasses by high-field, high-resolution 27Al NMR" J. Non-Cryst. Solids
275, 1-6.
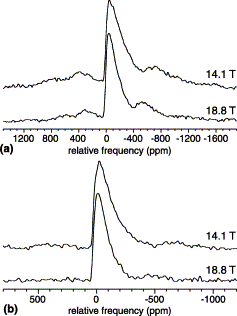
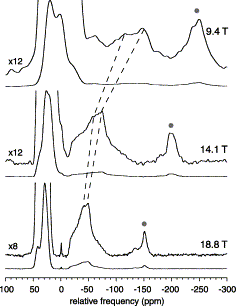
Details: Enhanced resolution and quantitation from "ultrahigh" field NMR spectroscopy of glasses Kroeker, S., Neuhoff, P.S. and Stebbins, J.F. (2000) " J. Non-Cryst. Solids 293-295 440-445. Abstract: The utilization of higher magnetic fields for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) (e.g., 14.1 and 18.8 T) can enhance both resolution and sensitivity in studies of disordered materials. When used in conjunction with fast magic angle spinning (MAS), high-field NMR can yield structural information not always available from NMR experiments of glasses at lower fields. Examples include site distinction of multiple boron groupings in 11B MAS NMR spectra of borate glasses, the spectroscopic observation of low concentrations of five- and six-co-ordinate aluminum species in 27Al MAS NMR spectra of aluminosilicate glasses, and new insight into magnesium co-ordination environments in silicate glasses using 25Mg MAS NMR. Also presented are 17O MAS NMR spectra of a zeolite in which high-field experiments permit resolution and quantification of bound molecular water. Comparisons of spectral data collected at 18.8 T with those at lower fields demonstrate these principles and indicate the potential of high-field MAS NMR applications to amorphous solids.
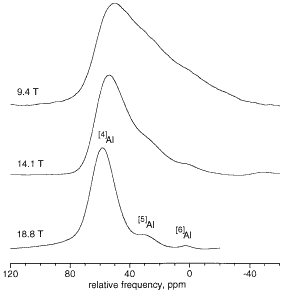
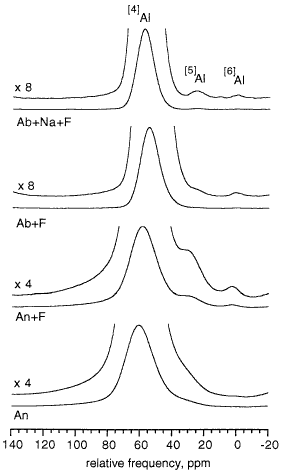
Quantification of five- and six-coordinated aluminum in aluminosilicate and fluoride-containing glasses by high-field, high-resolution 27Al NMR Stebbins, J.F., Kroeker, S., Lee, S.K. and Kiczenski, T.J. (2000) J. Noncryst. Solids 275, 1-6. Abstract: Aluminum cation sites with five ([5]Al) or six ([6] Al) anion neighbors are minor species in aluminosilicate glasses that are interesting in models of structure, diffusion, and viscous flow. Using 27Al NMR, we present the first direct evidence for [5]Al in a calcium-aluminosilicate glass without excess aluminum over charge-balancing cations, and quantify small concentrations of both [5]Al and [6]Al in several fluoride-containing aluminosilicate glasses. NMR techniques that enhance resolution by decreasing the effects of second-order quadrupolar broadening, including triple-quantum magic-angle spinning (3QMAS), analysis of spinning sidebands, and data collection at very high external magnetic fields (14.1 and 18.8 T), are particularly effective in accurately observing such species.
|
| Bio-X | Structural Biology | School of Medicine | Stanford University |